Guilford Techno Consultants, Inc
Claisen Condensation
Wednesday, April 19, 2023 by Guilford Techno Consultants, Inc. | Enolates
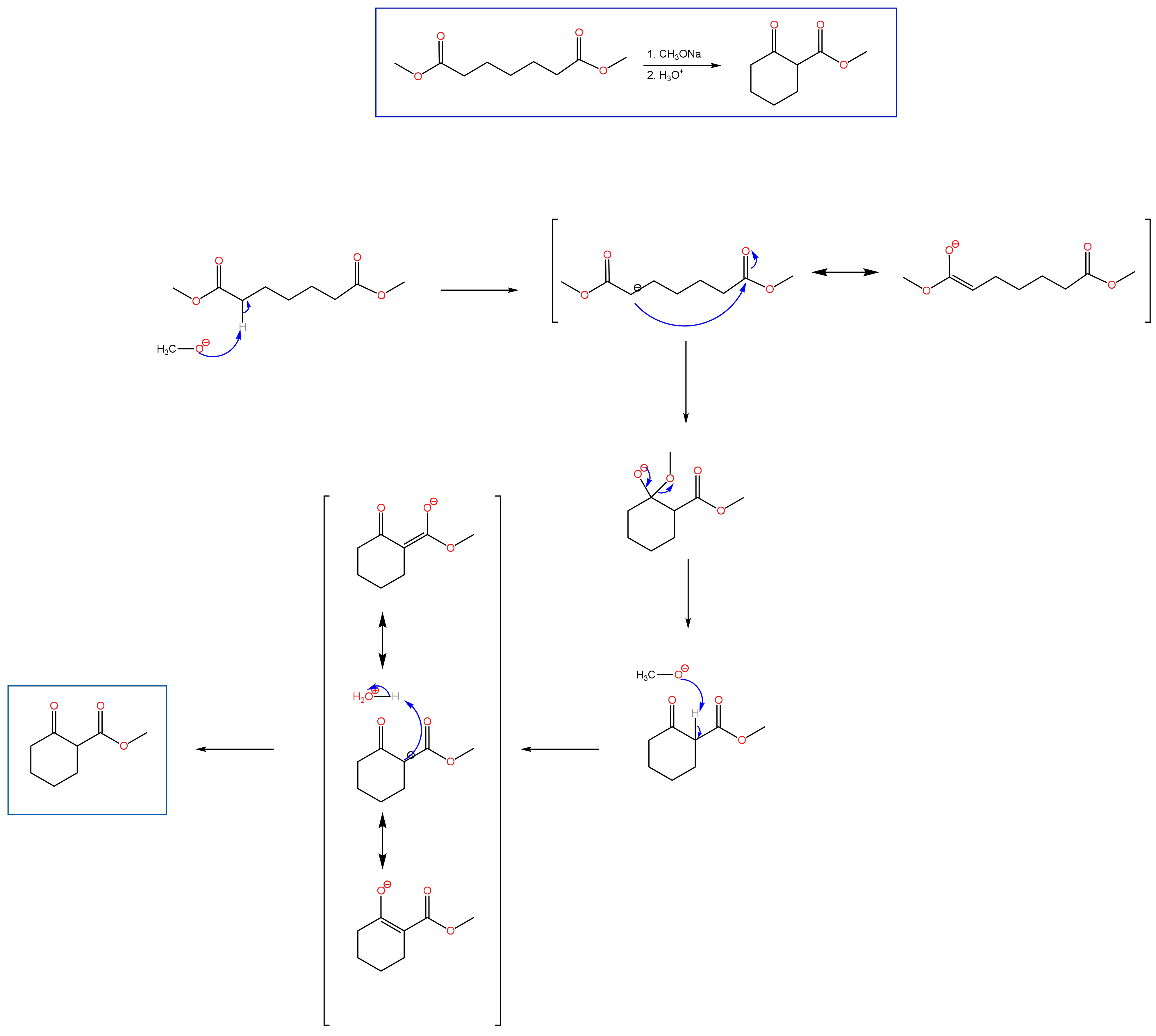
Carbonyl chemistry is a prominent part of the second semester of Organic Chemistry. An important component of carbonyl chemistry is reactions at the alpha carbon, such as the Aldol condensation that I spoke about in a previous post. Another condensation reaction covered in the second semester is the Claisen condensation. While an Aldol condensation is a reaction between aldehydes or ketones, the Claisen condensation involves the reaction of an ester with the enolate of another ester, a ketone, or aldehyde. If two esters are used as starting material, the product will be a β-keto ester. The resulting product from the condensation of an ester with a ketone will be a β-diketone. As with the Aldol condensation, the Claisen condensation can be performed with two moles of the same ester (self condensation). Unlike the Aldol condensation, the Claisen condensation involves two steps, the first being the generation of the enolate under basic conditions, followed by the subsequent attack of the second carbonyl compound to yield the product. After formation of the product, however, an acid step is needed to protonate the resulting alpha carbon between the two carbonyls. Below you will find the mechanism for the Dieckmann cyclization, which is an intramolecular Claisen condensation. Practice problems can be found under the OChem II tab.